How to increase the participation rate in your survey? Finding people to take a survey can be challenging. There are 4 reasons someone decides to participate (or not) in a survey. If you want to increase your survey response rate, consider these factors and follow our practical advice. Also, please read our article on the differences between professional and non-professional respondents.
Contact IntoTheMinds for your survey projects
TOP tips for increasing participation in your survey
- Offer financial compensation
- Clearly state what the research is about
- Explain how the answers will be valued
- Design a visually appealing questionnaire
- Design a survey that can be administered on mobile devices
- Keep your questionnaire concise: 9 minutes or 25 questions maximum
Sommary
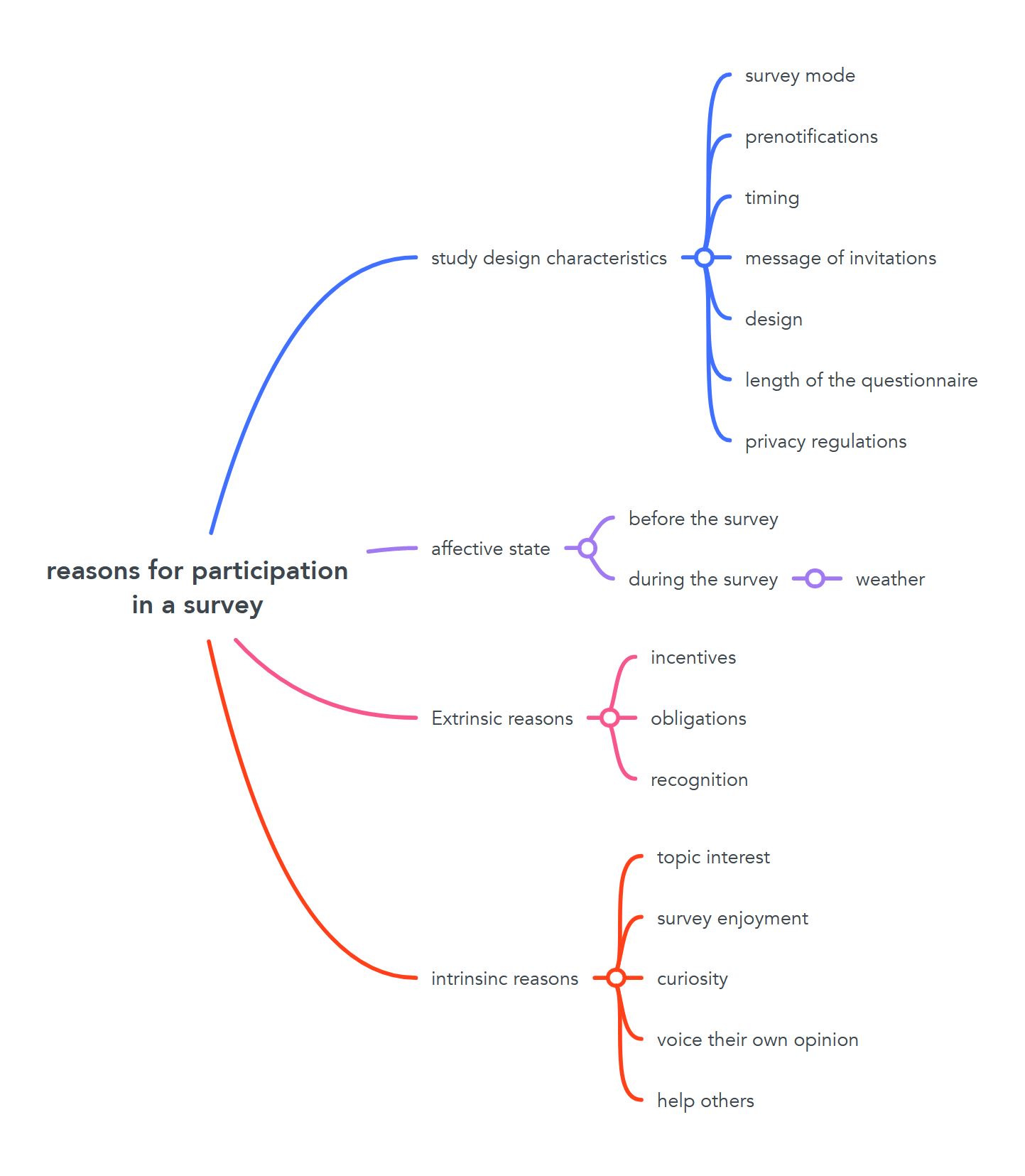
Intrinsic Reasons
Intrinsic reasons are those that are related to the person. These are reasons that you cannot influence. Here are 5 reasons to consider.
Interest in the topic
Interest in the subject of the survey is a key determinant of respondent participation. This is especially true for non-professional respondents. If you are using a convenience sample, then the responses to your survey will be particularly sensitive to this type of response.
Since the subject matter is an important factor, one of the most obvious practical tips is to explain the purpose of your survey when you distribute it.
Enjoying taking a survey
It may sound funny, but some people enjoy taking a survey. The enjoyment they experience is likely a composite of other aspects (see paragraphs below).
Curiosity
In 1995 research, Porst and von Briel showed that 15% of German lay respondents indicated interest and curiosity as their main motivation for participating.
Expressing their own opinion
My colleagues at IntoTheMinds recently carried out research for a government organization on the impact of energy prices. Evangelista et al. (1999) showed that 17% of Australian professional respondents were motivated by the potential to contribute to change. The respondents’ reactions were exactly that: they wanted to participate so their plight could be heard.
Altruism
This factor is often completely underestimated, but it is real. Some respondents want to help others, which is why they participate. This is often the case when students post their surveys on social networks.
Extrinsic Reasons
Extrinsic reasons for participating in a survey are those that are exerted on the participant. Here are 3 factors to consider.
Compensation
In a meta-analysis of the scientific literature on online surveys, Göritz (2006) showed that financial incentives motivate people to start and complete online surveys.
On the other hand, Messer et Dillman (2011) showed in experimental research that the response rate increases from 25.7% to 46.3% with a $5 compensation.
The financial incentive is, therefore, a powerful lever to increase the participation rate in your survey. This is what we do in our panel.
Recognition
Recognition from others can be one of the drivers of survey participation (Dillman, 2011). When you participate in a survey, especially from someone you know directly or indirectly, recognition is to be noticed. We often see this when we send a request to participate to someone we know. This is especially true in B2B surveys where the sample size is generally smaller, and invitations may be sent to respondents with whom you have a relationship.
Obligations
Krosnick (1999) suggested that some people may feel a social responsibility to participate. This is especially true when someone relays a survey. Consider, for example, a satisfaction survey sent by a department head to their staff or a student’s survey relayed to family members. This social pressure, personal or professional, is a powerful lever for participation.
Survey Design
The design of the survey itself is critical to ensuring high participation rates. Here are 7 factors to consider.
Method of survey
The survey method refers to how the survey is administered: via smartphone, desktop computer, or in person. The way a survey is administered has so much influence on the participation rate that we require our customers to carry out “mobile-friendly surveys.” The reason is that many people take advantage of their downtime to complete the survey: on public transport, between meetings, …
Pre-notifications (reminders)
The effect of reminders on survey participation is familiar. If you don’t send reminders, the likelihood of respondents forgetting to participate increases. Results from 97 research studies showed that the probability of participation increases when one or more reminders are sent. This was demonstrated in a meta-analysis (i.e., a research study) by Daikeler et al. (2020).
Timing
Timing is important in any research. Surveys are particularly sensitive to this, and you may be gambling the success of your project on the time of year you carry it out. We observe strong seasonality effects that affect the participation:
- during the summer vacations (July / August)
- during the end-of-year holidays
Weaker effects are observed during school vacations but do not represent an operational danger.
Invitation message
Please pay attention to your invitation message because it is the first point of contact between the respondent and the survey. It is important to make the respondent want to take the survey. If your message is poorly written, the participation rate of your survey will drop.
Clearly explain the context, why you are conducting this survey, how the responses will be valued, and what, if anything, is to be gained (see “compensation” paragraph above).
Design
The design of your survey is also important. It would be best to make your survey attractive to encourage people to participate. Unfortunately, we still see too many surveys carried out in Google that looks like endless Word files.
Remember that even in Google Forms, you can liven up your surveys with images.
Here are some rules to keep in mind:
- divide the questions over several pages so that the task (answering the survey) does not seem impossible
- identify the different sections with a larger font
- Don’t hesitate to use an illustrative image so that the different sections of your questionnaire are identified
Length of the questionnaire
We cannot repeat it often enough: the shorter your questionnaire, the higher the participation rate. Unfortunately, this obvious fact is often forgotten. We are always surprised when customers ask us to administer 30-minute questionnaires (true!).
Our rule of thumb is simple: 9 minutes or 25 questions maximum. Beyond that, your abandonment rate will increase significantly. We also advise against creating surveys that are too short. A survey that is too short (e.g., 5 questions) needs to clearly distinguish speeders, i.e., people who answer without thinking and whose response time is less than 1/3 of the median.
Privacy regulations
In the age of GDPR, privacy is important. It is, therefore, necessary to reassure participants. In an online context, Keusch et al. (2019) showed that consent for passive mobile data collection depends on respondents’ privacy and security concerns. However, another research published in 2023 nuances these results and shows that, in practice, respondents are little concerned about data privacy aspects.
The emotional state of the participant
This is something you can’t control. Nevertheless, research shows that emotional state influences the survey participation rate.
Before the survey
Stoop (2012) suggested that respondents are more easily recruited for a survey interview if they are in a good mood.
During the survey
Researchers have found that the weather during the interview influences survey results (Kämpfer et Mutz, 2013 ; Schwarz et Clore, 1983).
Posted in Research.