Conducting market research with ChatGPT has become an essential shortcut for many students and professionals. Using ChatGPT for market research is risky and raises many questions. Is the data provided by ChatGPT accurate? Is it complete? Does ChatGPT answer questions by reproducing the behavior of an average consumer? Harvard Business School’s Ayelet Israeli and her two co-authors have researched these questions. A. Israeli gave some (partial) answers in an online seminar I attended. In this article, I explain her experiments and what you can learn about using ChatGPT for market research.
Contact IntoTheMinds market research agency
Before getting to the heart of the matter, it’s necessary to lay down a few basics. ChatGPT is the chatbot interface for interacting with GPT4. GPT4 is a Large Language Model (LLM) belonging to the generative artificial intelligence family. LLMs predict the next most likely word to make up a sentence. To achieve this, they are trained on massive text corpora, enabling them to anticipate all possible combinations. It is, therefore, essential to understand that the answers provided by ChatGPT are conditioned by the texts already ingested. Despite popular belief, generative AI cannot “innovate.” It is constrained by the data on which it has been trained.
Let’s get to the heart of the matter. In the rest of this article, I’ll use “GPT” to refer to the LLM and ChatGPT to refer to the interface used to interact with GPT.
At this stage, GPT can only be used to emulate known behaviors. It can therefore be useful for answering simple questions in well-established sectors and for available products.

Market Research: 1000 ways to use GPT
Talking about using GPT for market research could be more specific. There are 1,000 ways of using generative AI to analyze a market. Here are just a few of them:
- writing an interview guide for an interview
- compose a form for an online survey
- writing desk research
- analyzing raw data with a plugin for chatGPT
What Ayelet Israeli proposes in her research is an even different approach.

Can GPT be used to “emulate” human behavior?
The interest of A. Israeli’s work lies in using GPT to “emulate” human behavior. In other words, she used chatGPT to obtain answers to questions that would have had to be asked of real consumers in conventional market research. So, she tested whether GPT behaved like a human and whether the answers provided matched economic theories.
I’ll discuss the limitations of this approach later in this article, but for now, I propose to detail two of the six experiments she carried out.
Price sensitivity: how does GPT react?
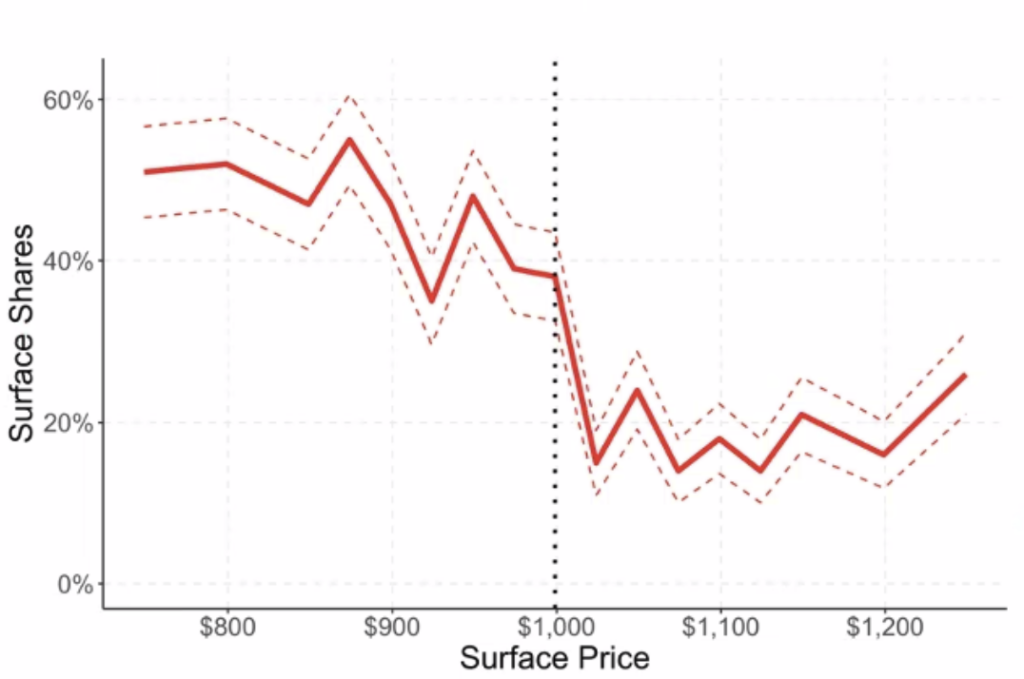
In the first group of experiments, the authors asked GPT to choose between two products (laptops) and varied the price of one of the two products. The aim was to understand which of the two the artificial intelligence would choose and to determine whether the choices followed a certain economic logic.
The question was as follows.
The authors varied the price of the first computer (“Surface Laptop 3”) in $1 increments between $750 and $1250. The graph below shows the evolution of the choice of the “Surface Laptop 3” model as a function of price.
The $999 mark (corresponding to the price of the competitor’s computer) represents a breaking point. Suddenly, GPT prefers the competing model in 80% of cases.
The authors conclude that GPT’s responses align with economic theory, which states that preferences change with price. However, it remains to be demonstrated that these responses align with actual consumer behavior. Let’s remember that consumers aren’t rational, and I can’t help but be surprised that at $750 (i.e., 25% less than the competing model), GPT chose the Surface Laptop 3 in only 50% of cases.

Propensity to pay: are GPT’s answers credible?
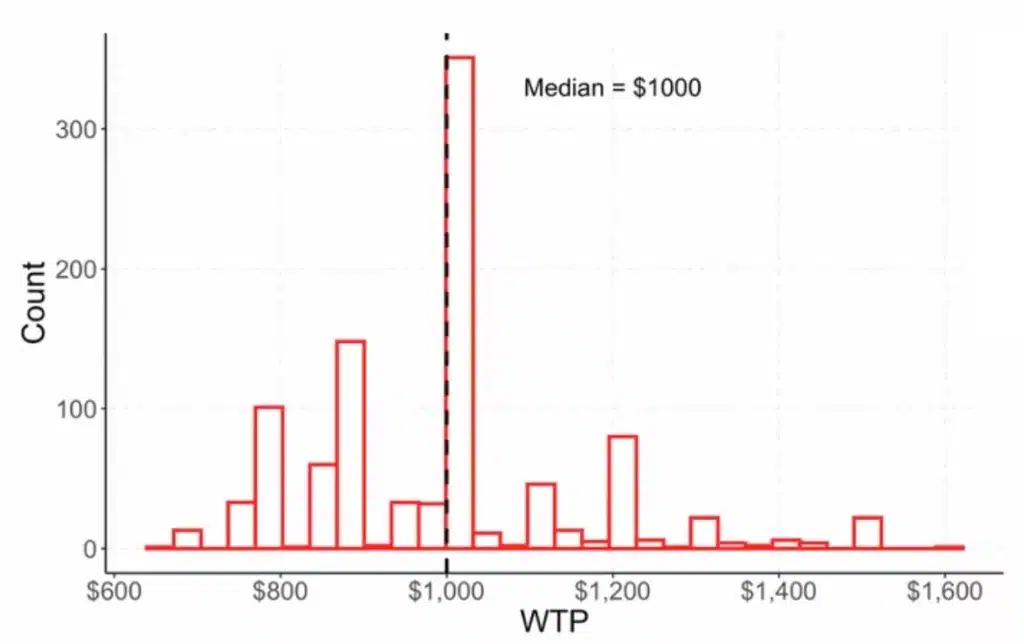
In another series of experiments, the authors tested “Willingness To Pay” (WTP) for several product types. The experiment consisted in describing a product to WTP and asking it what maximum price it would be willing to pay. By repeating the operation hundreds of times, the authors obtained a distribution compared with a theoretical distribution. The question asked was as follows.
They concluded that GPT’s answers were again in line with economic theory by displaying a distribution that could have corresponded to reality.
3 GPT’s limitations in carrying out market research
This research is part of pioneering studies into LLMs (Large Language Models) and GPT behavior. Their operation remains largely unknown, and much work will have to be carried out over the next few years to unravel their mysteries. There are many limitations to GPT, and these must be borne in mind when using it for non-recreational purposes such as carrying out market research. I see at least 3 major limitations:
- The authors assessed GPT’s behavior but not the correctness of its responses.GPT reacted correctly to the barrier price level, and the distribution of its responses was credible. But what about the accuracy of the responses? Are the prices fair? Does choosing one product over another correspond to what a human would have done?
- This type of experiment is limited to agreed-upon scenarioswidely covered in the literature and for which GPT has a training corpus. Market research carried out in this way with GPT can, therefore, only be applied to current products that are the subject of regular experimentation: fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), electronics, and energy.
- A major question remains as to what the results of this type of market research mean.What does GPT do when asked a question? Does it imitate human behavior? Or does it pick and choose from its corpus to display “probable” answers?

Final thoughts and conclusions
My final thoughts will inevitably focus on the widespread use of generative AI (and ChatGPT in particular) to conduct market research. At this stage, GPT can only be used to emulate known behaviors. It can therefore be useful for answering simple questions in well-established sectors and for available products. ChatGPT can never be reliably used to answer innovative product or service questions. Therefore, conducting a product-market fit analysis for an innovative product with ChatGPT makes no sense.
The only way to answer complex questions in uncertain environments is to collect ad hoc data. This involves primary data collected either qualitatively (interviews, focus groups) or quantitatively (CAWI, for example).
The hype surrounding generative AI is unhealthy. Basic precautionary principles are being forgotten, and everyone is lulled into thinking and doing just about anything. You only have to look at the company’s shadow GPT practices to be convinced that something is wrong. In such complicated times, it’s essential to keep a cool head and not make any mistakes.
Posted in Research.