What does privacy mean in the age of robots, articifial intelligence and omnipresent algorithms?
How do users percive privacy and how is it traded off against other benefits (personalization for instance)?
Those are still emerging questions that a team of marketing researchers from the University of Toulouse (France) tried to answer at the 2018 EMAC conference that was helf in Glasgow. More specifically the study looked at the factors influencing the “sharing frequency” as a dependent variable.
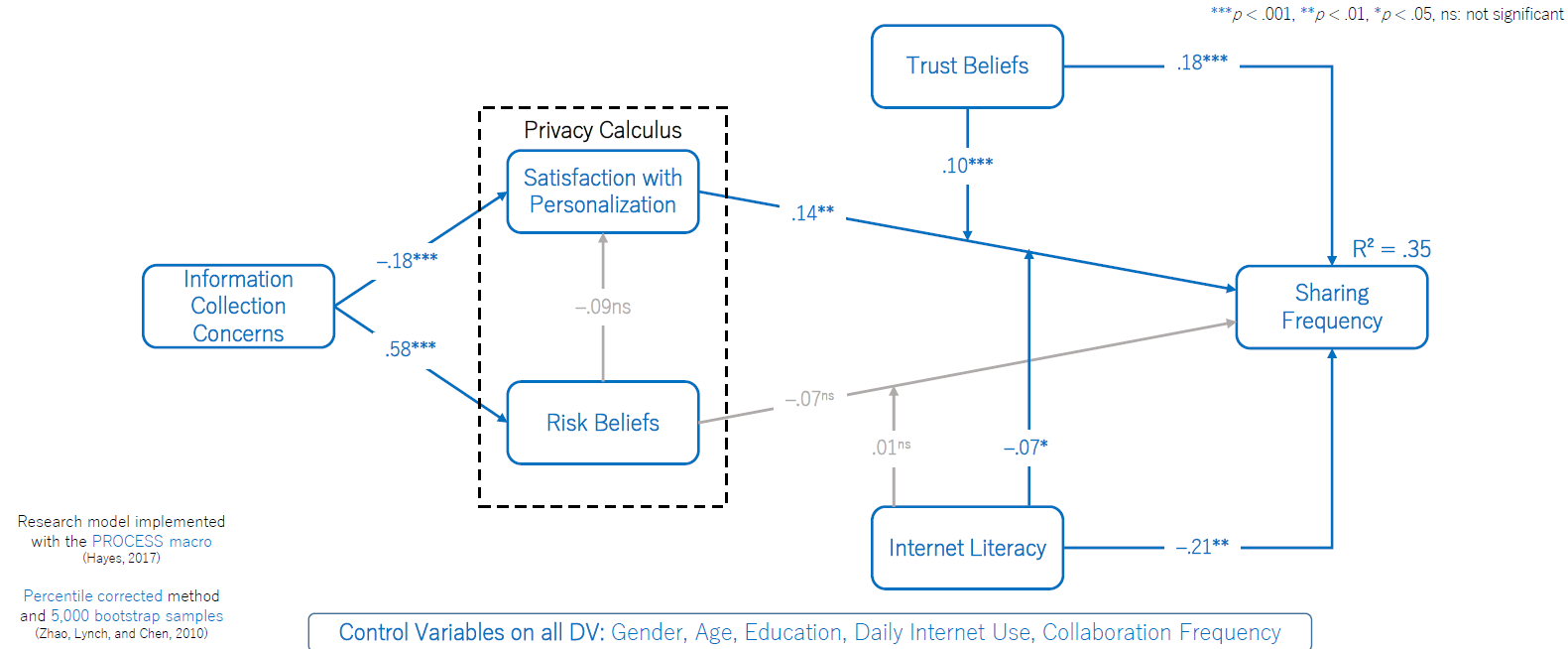
The results show that concerns on the information collected decrease user satisfaction with personalization and increase perceived risks. Interestingly satisfaction is positively moderated by trust beliefs and negatively affected by the user’s internet literacy.
Which factors are known to influence the perception of privacy?
The marketing research does a very good job at highlighting the factors which might influence consumer behavior and at articulating them into a model that is reasonnably simple and makes a lot of sense.
On the left-hand part of the model the direct effects of the information collected on the user are modeled against user satisfaction with personalization on the one hand, and risk beliefs on the other hand. Logically there is also a one-direction effect to be investigated from the risk perceived towards the user satisfaction. Risk and satisfaction are indeed the two faces of the same coin, where customer satisfaction is a trade off between what he obtains (personalization) in exchange of his data versus the risk perceived in sharing the data.
This “privacy calculus”, inconsoucly processed by the user will influence the sharing frequence which, the authors claim, is a proxy for loyalty.
On top of those direct effects, the moderating effects of trust beliefs and internet literacy are also researched.
The results
An online survey was conducted with a panel of 627 respondents that were representative of the French population
The results should be read in two phases : direct effects on the one hand, moderating effects on the other hand.
Direct effects
Not unsurprisingly the concerns expressed by the user with regard to the information collected decrease his satisfaction with personalization and increase the risk beliefs. In turn, thr higher the satisfaction, the higher the sharing frequency.
Moderating effects
It could be proved that while trust beliefs had a positive effects on sharing frequency, internet literacy had a negative moderating effect.
Conclusion
This marketing study nicely sums up the variables of importance that should be taken into account in the context of algorithmic recommendation.
The information collected on the users was shown to influence risk beliefs and satisfaction, which could be expected. The effects of trust and internet literacy on satisfaction and loyalty should lead managers to think about their efforts to be trusted by their clients and how they convey this feeling of trust as far as data collection and exploitation is concerned.
The trust factor is also a good news for the public service sector which usually benefits from higher trust than its commercial counterparts.
Image : Shutterstock
Posted in Research.